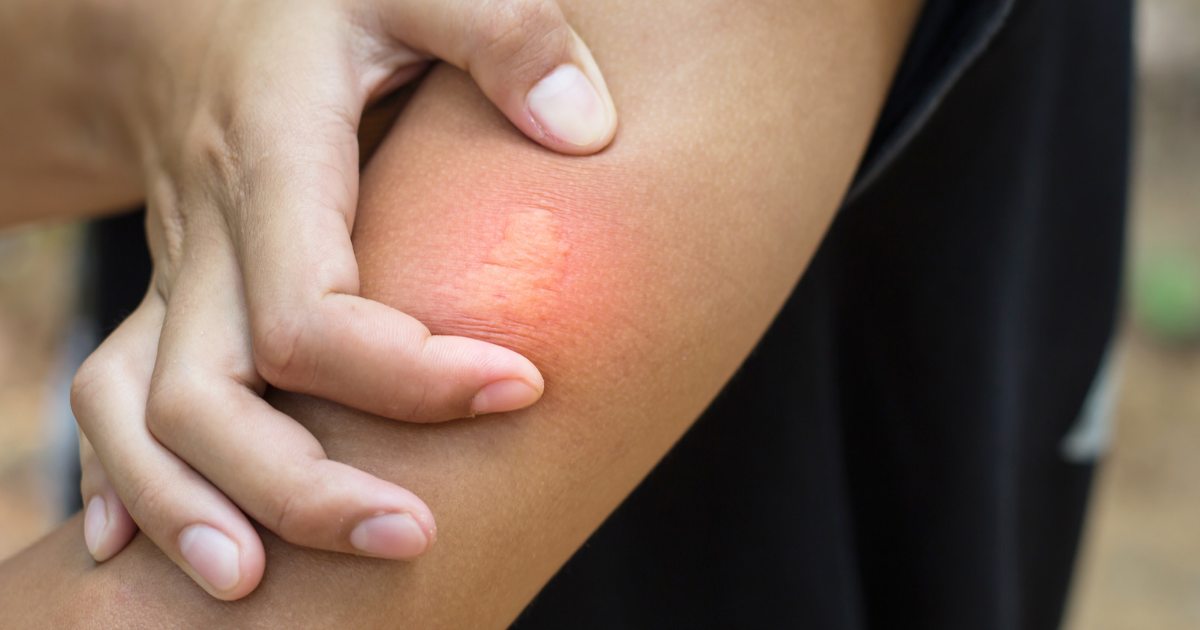
Though they are relatively small, bees are able to pack a powerful punch with their stingers. For those who are allergic to bee stings, a single sting can be incredibly dangerous and even life-threatening. For everyone else, a bee sting is still painful and can cause swelling, redness, and irritation.
Signs of Generalized Allergic Reaction to Bee Stings
Generally, bee stings result in a local reaction that causes pain, swelling, and redness at the site of the sting. For some people, however, bee stings can trigger a more serious, generalized allergic reaction. Signs of a generalized allergic reaction include swelling of the face, lips or throat; difficulty breathing; hives; lightheadedness or dizziness; nausea or vomiting. If you experience any of these symptoms after being stung by a bee, seek medical attention immediately.
Causes of Generalized Allergic Reactions to Bee Stings
While the exact cause of generalized reactions to bee stings is not known, it is believed that they are caused by an overreaction of the immune system. When a person with a sensitivity to bee venom is stung, their immune system produces antibodies to fight off the bees’ venom. These antibodies then release chemicals into the bloodstream that cause symptoms such as swelling, hives, and difficulty breathing. In some cases, these reactions can be life-threatening.
Who Is at Risk for Generalized Allergic Reactions?
Anyone can have a generalized allergic reaction to a bee sting, but some people are more at risk than others. People who have previously had a localized reaction to a bee sting are more likely to have a generalized reaction if they are stung again. People with other allergies, such as hay fever or food allergies, are also more likely to have generalized reactions.
Treating Generalized Allergic Reactions
If you have been stung by a bee and are experiencing symptoms of a generalized allergic reaction, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. The most effective treatment for an allergic reaction is epinephrine, which is available in an injection form (EpiPen). Epinephrine works quickly to reduce symptoms and can be life-saving if administered in time. If you have been prescribed an EpiPen, be sure to carry it with you at all times in case of an emergency.
Bee stings usually only result in localized reactions like pain and swelling. However, some people may have a more serious systemic reaction known as anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis typically occurs within minutes or hours after being stung and can cause potentially life-threatening symptoms such as difficulty breathing and low blood pressure. If you experience any indications of anaphylaxis after being stung by a bee—such as swelling of the face or throat; hives; difficulty breathing; lightheadedness or dizziness; nausea or vomiting—seek medical attention immediately and use your EpiPen if necessary.
Best way to treat a bee sting?
Read on to find out
1. Remove the stinger
If you’ve been stung by a bee, the first thing you’ll want to do is remove the stinger. You’ll want to act quickly as well—the longer the stinger stays in your skin, the more pain and irritation you’ll experience. To remove the stinger, simply scrape it off with your fingernail or a credit card. Once the stinger has been removed, wash the area with soap and water.
2. Apply a cold compress
After you’ve removed the stinger and cleansed the area, you’ll want to apply a cold compress to help reduce swelling and pain. A cold compress can be made simply by wrapping ice in a clean cloth or using a bag of frozen peas or corn. Apply the cold compress for about 10-15 minutes at a time. Repeat as necessary for pain relief.
3. Take an antihistamine
If you’re experience swelling and redness around the site of the sting, you may be having an allergic reaction. In this case, you’ll want to take an antihistamine such as Benadryl to help reduce your symptoms. Be sure to follow the directions on the package for proper dosing instructions. If your symptoms persist or worsen after taking an antihistamine, seek medical attention immediately as you may be going into anaphylactic shock.
Conclusion
Most bee stings will heal on their own within a few days with home treatment measures such as those outlined above. However, if you’re experiencing severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swallowing, chest tightness, confusion, or fainting, seek medical attention immediately as these could be signs of anaphylactic shock—a potentially life-threatening reaction to a bee sting.